Kidney stones are one of the most common urology problems in India, especially in hot regions like Rajasthan where dehydration is very common. Millions of people search every month “how are kidney stones formed” to know why this condition develops. According to leading experts from the best urology hospital in Jaipur, kidney stones are formed when minerals in the urine become too concentrated and start to crystallize. Understanding the science behind it can help you prevent early and keep your kidney healthy.
This detailed blog explains:
- How kidney stones exactly formed
- Who is at highest risk
- Symptoms you should never ignore
- Types of kidney stones
- Prevention tips
- Latest treatments like Laser & RIRS
Let’s begin.
What are kidney stones?
Kidney stones are solid mineral crystals and we know this as a stone that develops inside the kidney when specific substances in urine become highly concentrated and start combining.
These substances include:
- Calcium
- Uric Acid
- Cystine
- Oxalate
- Phosphate
When these substances cluster together and crystallize, then they are gradually turn into a hard stone.
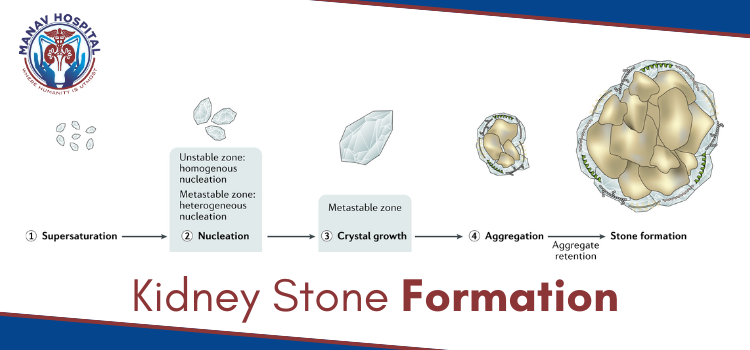
How Are Kidney Stones Formed? (Simple Scientific Explanation)
The process of kidney stone formation happens in 3 steps:
Step 1: Concentrated Urine
When you drink less water or live in a hot climate, your urine becomes thick and concentrated.
Step 2: Mineral Crystallization
Excess minerals like calcium, oxalate, uric acid stick together and form tiny crystals.
Step 3: Crystals Grow into Stones
Over time, these crystals combine and grow into small or large stones.
What Increases Your Chances of Stone Formation?
People often ask “how are kidney stones formed so easily?”
Here are the major risk factors:
1. Drinking less water
The biggest reason in Indians.
2. High salt intake
Salt increases calcium in urine.
3. High-oxalate diet
Spinach, beetroot, chocolate, nuts.
4. Hot climate
More sweating → less urine → stones.
5. Genetics
Family history increases risk.
6. Excess protein
Non-veg & supplements worsen it.
7. Obesity
Slows kidney filtration.
8. Uric acid elevation
Common in diabetic/overweight patients.
9. Certain diseases
- Thyroid problems
- Repeated UTIs
- Crohn’s disease
Types of Kidney Stones & Why They Formed
| Stone Type | How They Formed | Who Gets Them |
| Calcium Oxalate | Low water, high oxalate diet | Most common in India |
| Uric Acid Stones | High protein diet + acidity | Non-veg eaters, diabetics |
| Struvite Stones | After repeated infections | Women with UTIs |
| Cystine Stones | Genetic disorder | Rare cases |
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
If you’re wondering how kidney stones formed, you should also know the signs:
- Severe back or side pain
- Pain radiating to lower abdomen
- Burning urination
- Blood in urine
- Nausea & vomiting
- Frequent urination
- Fever (infection risk)
👉 Pain that comes in waves = strong sign of moving stone.
How Doctors Diagnose Stones
An experienced urologist doctor checks:
- Ultrasound
- Urine Test
- CT scan
- X-ray
- Kidney function test
How Are Kidney Stones Treated?
Treatment depends on size, location, and pain level.
1. Small Stones (<5mm)
- Medicines
- Hydration
- Pain control
2. Medium Stones (6–10mm)
- Laser treatment
- RIRS
- Lithotripsy (ESWL)
3. Large Stones (>15mm)
- PCNL surgery (Minimally invasive)
- Hospital admission may be needed
Modern urology ensures no cuts, no stitches, fast recovery.

Diet: What Causes Kidney Stones vs What Prevents Them
Foods that increase stone formation:
- Spinach
- Beetroot
- Chocolates
- Nuts
- Tomatoes
- Excess milk
- Fast food
- Excess salt
Foods that prevent stones:
- Lemon water
- Coconut water
- Cucumber
- Watermelon
- Low-salt diet
- More water (2–3 liters daily)
How to Prevent Kidney Stones (Doctor Recommended)
- Drink 8–10 glasses of water
- Reduce salt
- Avoid too much protein
- Limit oxalate-rich foods
- Maintain weight
- Avoid dehydration
- Check urine infections
- Get annual kidney checkup
When to Visit a Urology Specialist?
Go to a urologist or a urology hospital in Jaipur if:
- Pain lasts more than 6–8 hours
- Vomiting doesn’t stop
- You see blood in urine
- High fever (dangerous infection)
- You cannot pass urine
- Previously had stones
Early treatment can give you a healthy life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Kidney stones symptoms often include severe pain in the lower back or side, pain while urinating, cloudy or bloody urine, nausea, vomiting, and frequent urination. In some cases, kidney stones may not cause symptoms until they start moving inside the urinary tract.
The kidney stones etiology mainly involves dehydration, high mineral concentration in urine, dietary habits, metabolic disorders, and family history. When substances like calcium, oxalate, or uric acid become concentrated, they can crystallize and form stones.
Kidney stones pain is often described as one of the most intense pains. It usually starts in the back or side and may radiate to the lower abdomen and groin. The pain can come in waves and change in intensity as the stone moves.
Yes, kidney stones symptoms in females may sometimes be confused with gynecological issues. Women may experience lower abdominal pain, pelvic pain, burning during urination, frequent urge to urinate, and nausea, along with back or side pain.
Kidney stones removal depends on the stone size and location. Small stones may pass naturally with fluids and kidney stones pain relief medications. Larger stones may require kidney stones removal surgery, such as laser lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, or minimally invasive procedures recommended by a urologist.



